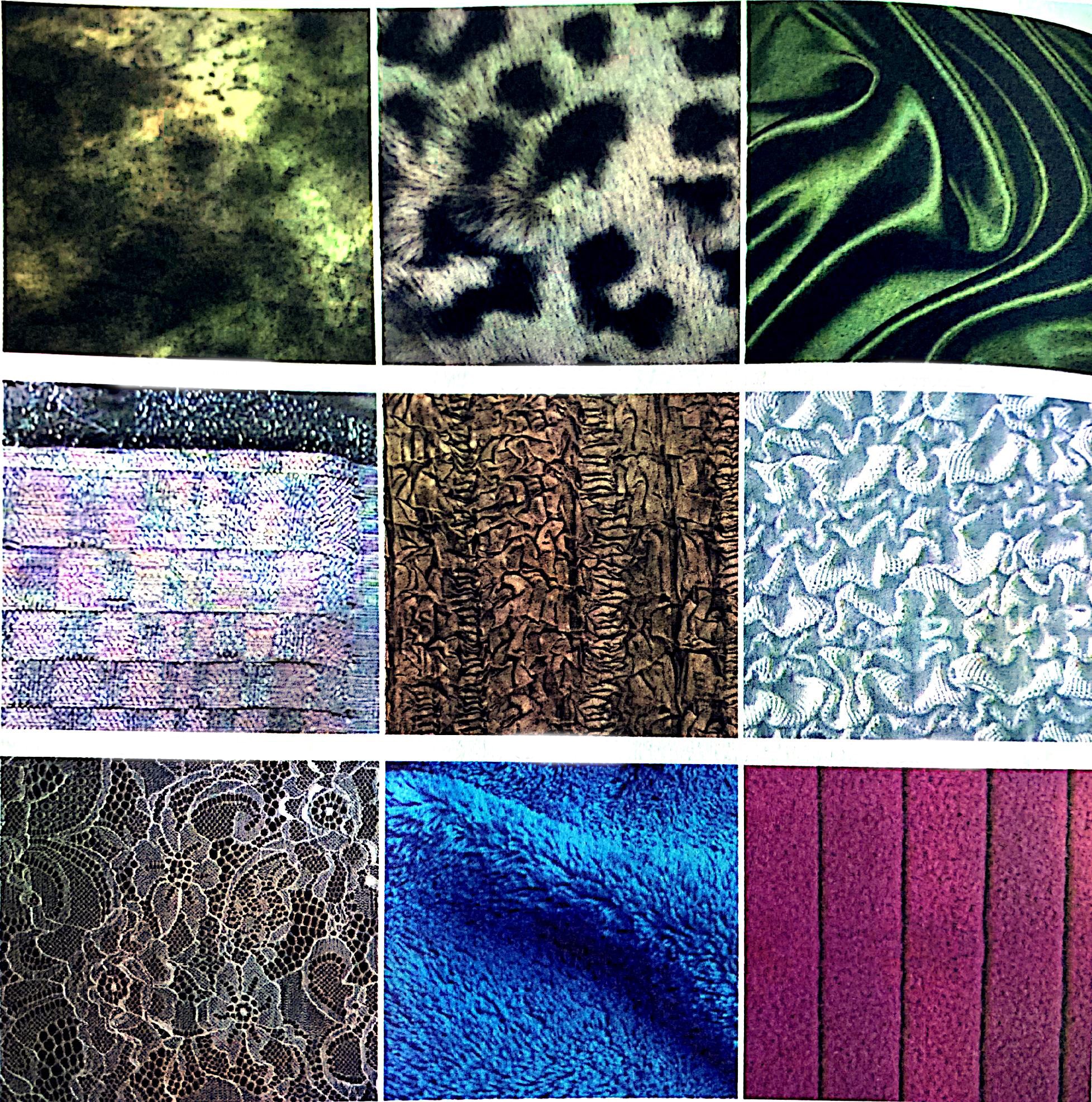
Regenerated fiber fabrics
Regenerated fiber fabrics refer to fabrics made from various recycled fiber materials mainly composed of viscose fibers. There are viscose fiber fabrics, copper ammonia fiber fabrics, acetate fiber fabrics, Tencel fiber fabrics, Modal fiber fabrics, milk silk fiber fabrics, soybean fiber fabrics, peanut silk fiber fabrics, as well as their blends and interweaving fabrics.
The intrinsic properties of regenerated fiber fabrics
The main performance characteristics of regenerated cellulose fiber fabrics are hygroscopicity, breathability, and dyeing properties. The fabric is soft, smooth, hygroscopic, sweat permeable, and comfortable to wear. After dyeing, the color is bright and the color fastness is good. Regenerated fiber fabrics, like natural fiber fabrics, have the properties of shrinkage and susceptibility to mold and decay after washing, but have the disadvantages of washing fading and elasticity that are not as good as synthetic fibers. Regenerated fibers do not have thermoplastic properties. Artificial protein fiber fabrics have properties similar to wool, with a soft and elastic feel, good warmth retention, and comfortable wearing.
Appearance style of regenerated fiber fabrics
Regenerated fiber is a type of chemical fiber that is made using chemical methods, so its form is variable. The fiber can be either long or short, and can be shiny or dull. The appearance style of its fabric is also diverse.
The appearance style of regenerated fibers is similar to the fiber fabric it imitates. Viscose fibers are the main variety of regenerated fibers. Viscose fibers that mimic cotton (artificial cotton) have the appearance characteristics of cotton fiber fabrics, while viscose fibers that mimic wool (artificial wool) have the appearance characteristics of wool fiber fabrics. Viscose fibers that mimic silk (artificial silk) have the appearance characteristics of silk fiber fabrics. Viscose fibers are soft, with good drapability and anti pilling properties, but they are easy to break.
Examples of regenerated fiber fabric fabrics
Most chemical fibers are mainly made of natural fiber like fabrics and can be mixed and interwoven with various fibers, resulting in various types of cotton and viscose fabrics, viscose linen, polyester and viscose wool like fabrics, woolen and viscose tweeds, viscose and nylon ice silk fabrics, burnt velvet, rayon crepe de chine, rayon georgette, spandex printed silk, spandex lining, Tencel blended fabric, modal underwear, milk silk underwear, acetate silk fabric, etc.
The changes in regenerated fiber fabrics are greater than those in natural fibers, and the variety is very diverse. Different styles of regenerated fiber fabrics are shown in the figure.
Synthetic fiber fabric
Synthetic fiber fabrics refer to various synthetic fiber fabrics mainly made of polyester, nylon, and acrylic fibers. The largest consumers are pure, blended, and interwoven fabrics of polyester. Specifically, there are polyester cotton like fabrics, polyester linen like fabrics, polyester wool like fabrics, polyester silk like fabrics, etc. There are polyester cotton blended fabrics, wool polyester and polyester wool blended fabrics, polyester linen and polyester blended fabrics, polyester viscose blended fabrics, polyester viscose blended fabrics, three in one and four in one fabrics blended with polyester and various fibers, etc. Polyester silk can also be interwoven with real silk and rayon, and mixed with cotton Hemp interweaving, wool interweaving, etc. Polyester can also be interwoven with hemp yarn for weaving, and with wool yarn for weaving. So, polyester is the most widely used in the field of clothing fabrics.
With the resurgence of nylon, nylon has replaced polyester in various blended, interwoven, and blended fabrics, such as nylon cotton blended fabrics, nylon viscose blended fabrics, interwoven fabrics, nylon silk interwoven, and blended fabrics. The variety of nylon fabrics is also constantly enriching.
In addition, there are pure, blended, and interwoven fabrics of acrylic fiber. Spandex and various types of fiber core-spun elastic fabrics, as well as spandex textured elastic fabrics, are widely used in underwear, tight fitting clothing, and fitting clothing.
Intrinsic properties of synthetic fiber fabrics
Synthetic fiber fabrics have high strength, good fastness, smoothness, firmness, elasticity, wear resistance, resistance to mold and insects, bright colors, and are not easy to fade. They have thermoplastic properties and are easy to wash and dry.
Synthetic fibers are not as comfortable to wear as natural fibers, with poor moisture absorption and permeability. Sweating feels stuffy and breathable, and fabrics are prone to generating static electricity, adsorbing dust, sticking to the body, generating sparks, and easily winding and pilling.
Synthetic fiber fabric appearance style
The appearance style of synthetic fibers is diverse, which can be the appearance of cotton fiber fabrics, dull and simple; It can have the appearance of hemp fiber fabric, rough and stiff; It can be the appearance of wool fiber fabric, fluffy and full; It can have the appearance of silk fabric, smooth and soft. With the development of biomimetic technology, synthetic fibers can mimic various natural fibers very much, but they are not natural fibers and their wearing performance is greatly different from that of natural fibers.
Synthetic fiber fabrics have good elasticity and a flat and neat surface; Colorful and not easily fading; The fabric has thermoplastic properties and can be set in one go; Poor hygroscopicity, prone to static electricity and pilling. The performance of synthetic fibers themselves will be integrated into imitated fiber fabrics.
Examples of Synthetic Fiber Fabric Fabrics